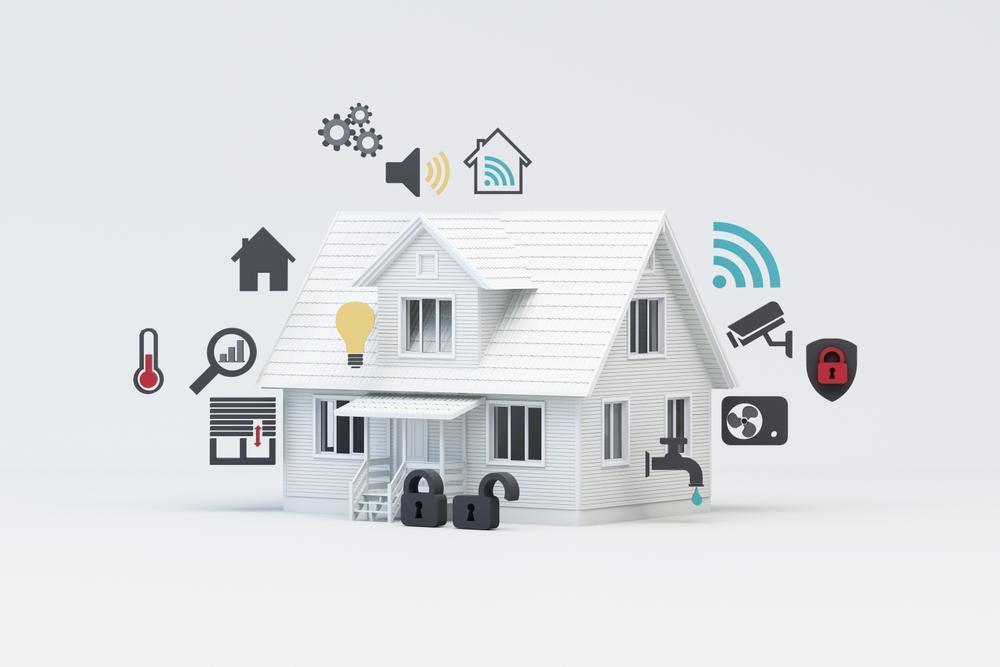
Smart homes require a reliable internet provider; A weak signal can cause smart bulbs to flicker, video feeds to freeze, or voice commands to drop out. When you set up a smart home, consider WiFi optimization carefully to boost coverage, reduce interference, and prioritize IoT devices for peak performance. Whether you’re just starting or looking to improve WiFi for an existing setup, these strategies will keep every corner of your smart home running smoothly.
1. Why WiFi Matters for Smart Homes
Every smart home gadget, from your voice-activated lights and connected thermostat to security cameras and smart dishwasher, relies on a steady Wi-Fi connection to communicate with other devices, obey voice commands, and upload information to the cloud. When your network lags or drops out, devices can become unresponsive, automated routines fail, and you can miss security alerts. Even routine tasks like scheduling your coffee maker or adjusting smart blinds can grind to a halt. WiFi optimization helps keep smart devices synchronized, secure, and reliable.
2. Assess Your Current WiFi Performance
WiFi optimization begins with internet speed tests near your router, upstairs, and in outdoor spaces to determine if your download and upload speeds fall below your plan’s promised performance. Note any dead zones or unusually slow pings that could interfere with smart device signals.
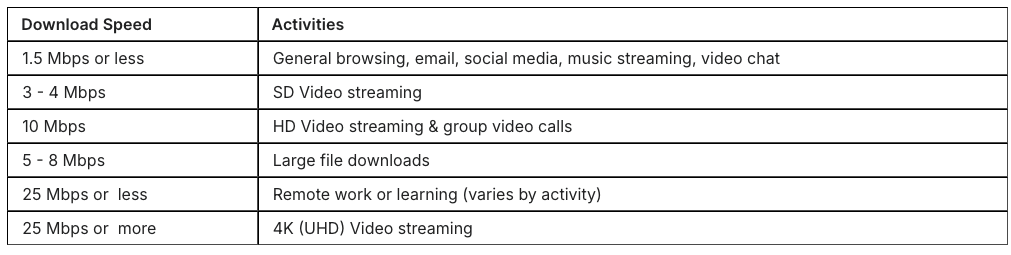
Source: Brightspeed.com | Internet Speed Test
Next, check your router’s placement. Is it tucked away in a cabinet, close to other electronics, or wedged in a corner? All these circumstances could compromise your wireless signal. Finally, confirm your subscription speeds with your ISP. If your real-world results consistently fall short, it‘s a sign to upgrade your plan to a higher-speed alternative, such as fiber internet.
3. Optimize Your Router Placement and Settings
Where you place your router has an impact on your wireless signal strength. To achieve the best results, consider the following :
- Place the router in a central, elevated location.
- Avoid placing the router next to thick walls, heavy furniture, metal objects, and large electronic appliances.
- Don’t hide your router in a cabinet or other enclosure, as this can disrupt the signal.
- If your router has antennas, experiment with their positioning to see if you can strengthen the WiFi signal.
You can adjust wireless channels through your router’s admin tools. Most routers default to busy channels, especially on the 2.4 GHz band. Use a free app or built-in scanner to identify the least crowded channels in your home, then switch to those channels to minimize interference from neighboring networks, cordless phones, or microwaves.
If your home is packed with smart devices, consider upgrading to a dual-band or tri-band router. Dual-band routers offer both 2.4 GHz (longer range) and 5 GHz (higher speeds). In contrast, tri-band routers add an extra 5 GHz network to spread out traffic and ensure your security cameras, smart speakers, and streaming devices all get the bandwidth they need.
4. Use WiFi Extenders or Mesh Networks
Larger homes or homes with challenging layouts may require WiFi extenders or Mesh networks to reach the edges of your property or eliminate dead spots in garages, outdoor living areas, and distant rooms. Both solutions create additional access points that improve coverage.
- Wi-Fi Extenders rebroadcast your router. They’re a budget-friendly way to patch dead zones, but work best when placed in locations where your existing network is still strong.
- Mesh Systems connect multiple satellite nodes to your main router. These nodes each act as routers, receiving and retransmitting signals to deliver consistent speeds throughout the network. Mesh networks are recommended for larger homes or complex layouts where walls, floors, or unusual designs impede signal flow.
5. Upgrade Your Internet Plan for Smart Home Demands
Smart devices are like eating chips: it’s hard to stop with just one. As you add security cameras, video doorbells, voice assistants, and streaming hubs, your network’s bandwidth needs climb sharply. A single 4K security camera can use 5–10 Mbps, while streaming UHD content eats up 25 Mbps or more. To keep everything running smoothly, a typical smart home requires at least 100–200 Mbps.
Where available, fiber internet is the gold standard, with symmetric upload and download speeds, minimal latency, and rock-solid reliability. Fiber’s consistent performance means your smart home automation, video conferencing, and streaming don’t have to compete for scarce bandwidth, and you won’t need to troubleshoot slow internet.
In the absence of fiber internet, fixed-wireless or cable upgrades deliver solid speeds. Rural internet options are more limited, but advances in satellite internet have improved latency and throughput, making them a viable option for smart homes with a limited number of devices. Always compare plans for actual speeds during peak hours, data caps, and pricing tiers.
Whichever ISP you choose, strong WiFi is the backbone of any efficient smart home system. To keep your smart home running smoothly, evaluate your current setup and implement some WiFi optimization strategies for peace of mind and better device performance.